covering Bedfordshire, Hertfordshire & Buckinghamshire
Garden Pond Cleaning
& Maintenance Services
At Aqua Pond Ltd, we provide comprehensive pond cleaning services tailored to different needs and budgets. Our solutions range from basic maintenance to complete pond overhauls.
speak with an expert today
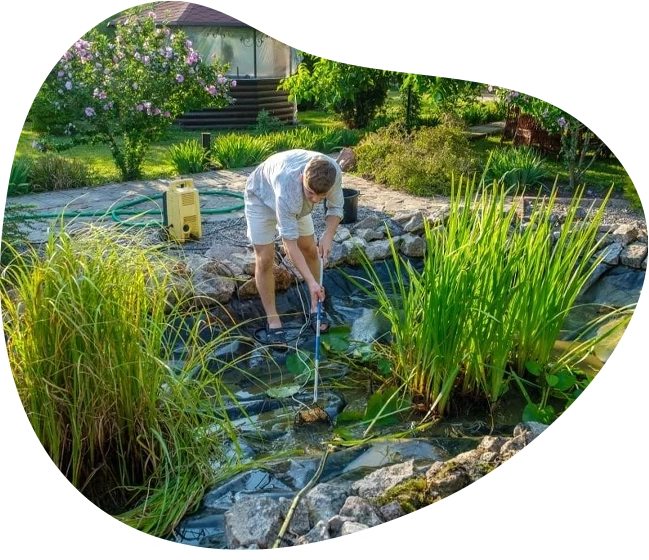



About Aqua Pond
We specialize in pond construction and maintaining koi ponds, ensuring optimal water conditions for these unique environments. We also include aquatic plants in our pond designs to enhance the natural beauty and ecological balance of your pond.
We also offer comprehensive maintenance services to keep your pond in optimal condition, including water quality management, algae control, and seasonal clean-ups for garden ponds of various sizes. We proudly use Oase pond products, which are known for their effectiveness in maintaining crystal clear water and their award-winning status in the pond care market.
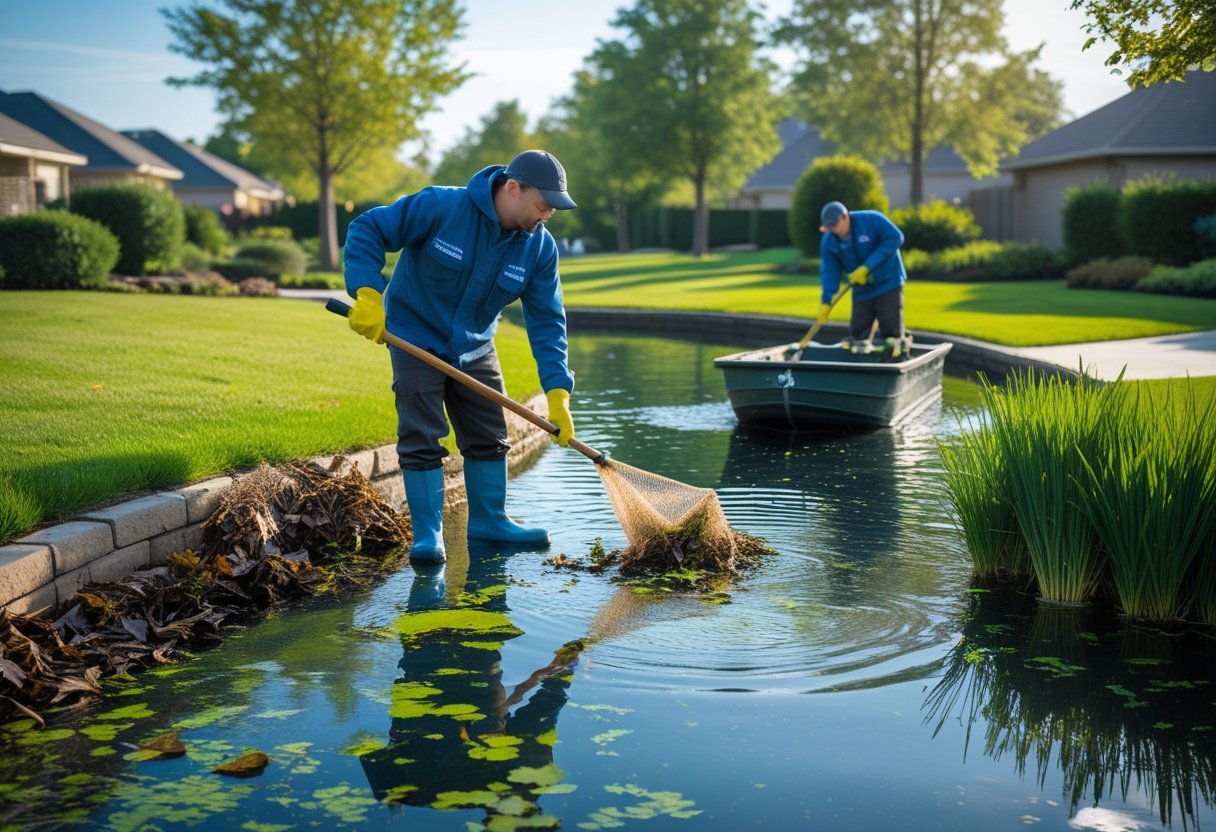
Pond Cleaning Service
Our Full Clean is a thorough service for ponds requiring comprehensive attention.
- We begin by carefully relocating your fish to temporary holding tanks with water from your pond to minimize stress.
- Next, we drain the pond completely to access the bottom surface.
- We remove accumulated silt, debris, and stubborn algae using specialized equipment. Our team thoroughly cleans the liner, rocks, and ornamental features. We inspect and clean all pond equipment, including pumps, filters, and UV clarifiers.
- Faulty components are identified and replaced if necessary.
- Before refilling, we check for any damage to the liner or structure.
- Finally, we treat the water with appropriate conditioners and gradually reintroduce your fish once water parameters are stable.
This comprehensive service is recommended annually to maintain optimal pond health.
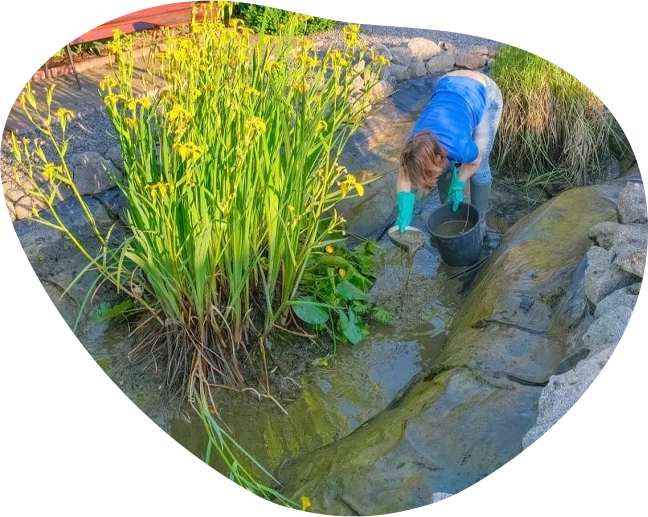
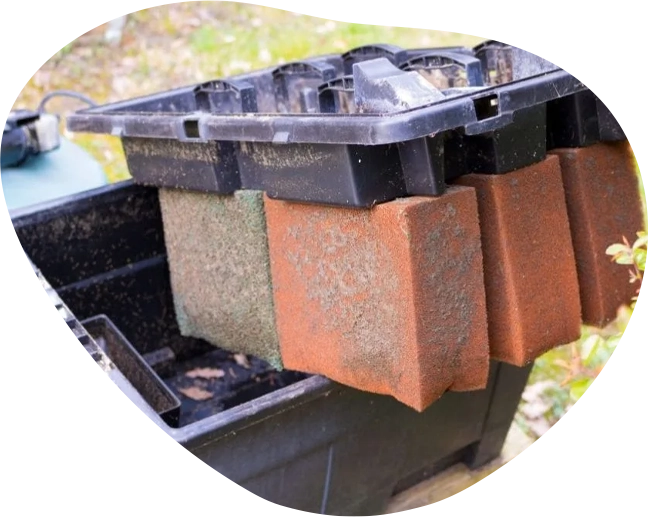







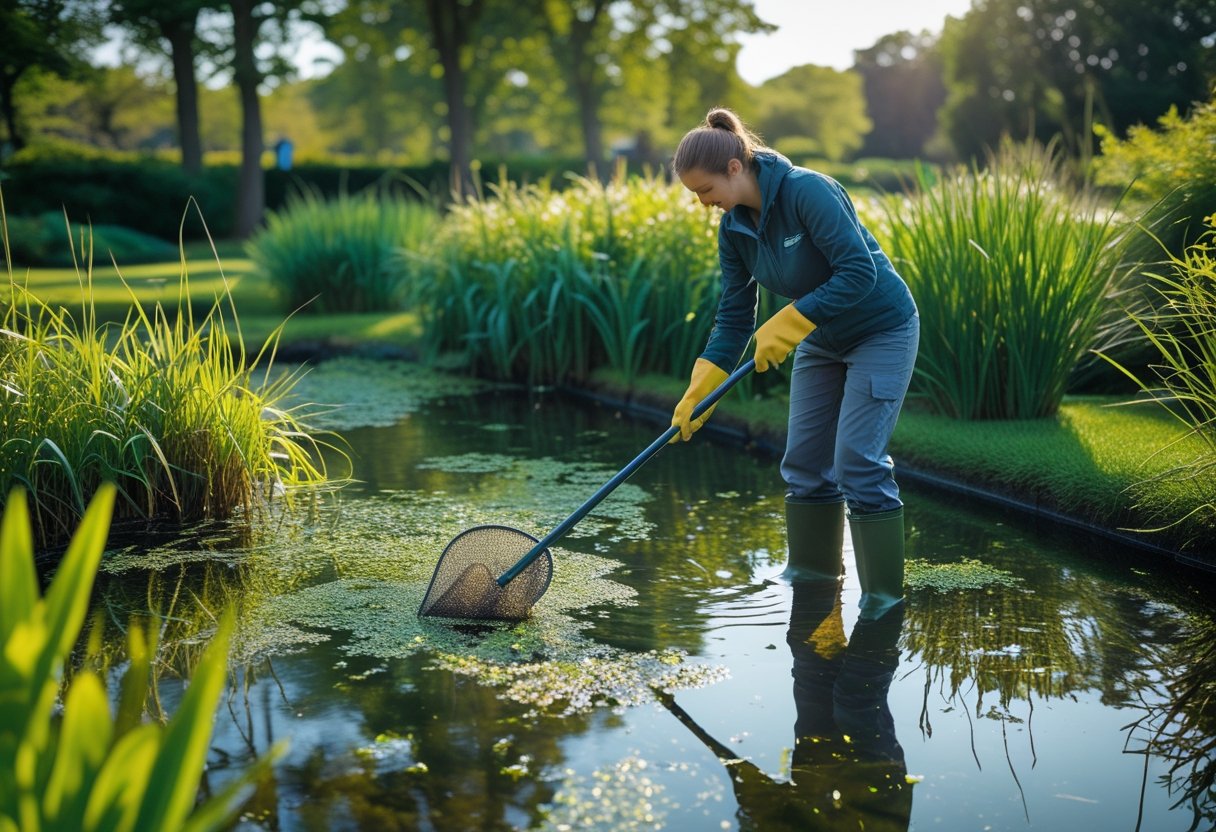
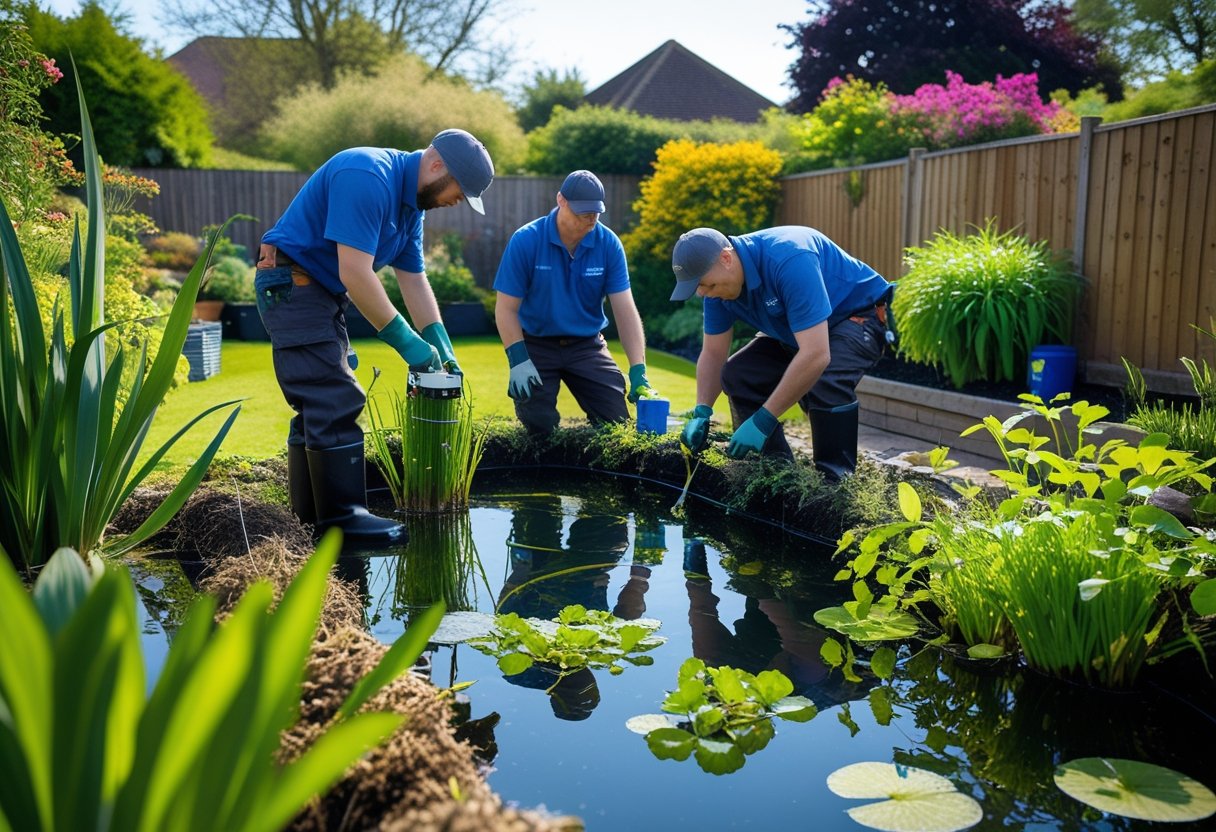
Pond Maintenance Services
We offer customised maintenance contracts to suit the specific needs of your pond.
Our team of skilled operators visits your property on a scheduled basis to perform essential tasks that keep your pond in optimal condition.
These visits typically include:
- Filter cleaning and maintenance
- Removal of debris and dead plant material
- Algae control treatments
- Equipment checks and minor repairs
Our pond maintenance services ensure your pond remains balanced and healthy, preventing common issues before they develop.
We recommend monthly visits during the growing season and less frequent maintenance during winter months.
Each visit is documented, and we recommend any additional treatments or repairs that might be needed.
Our experienced team can advise on fish health and plant care during these regular visits.

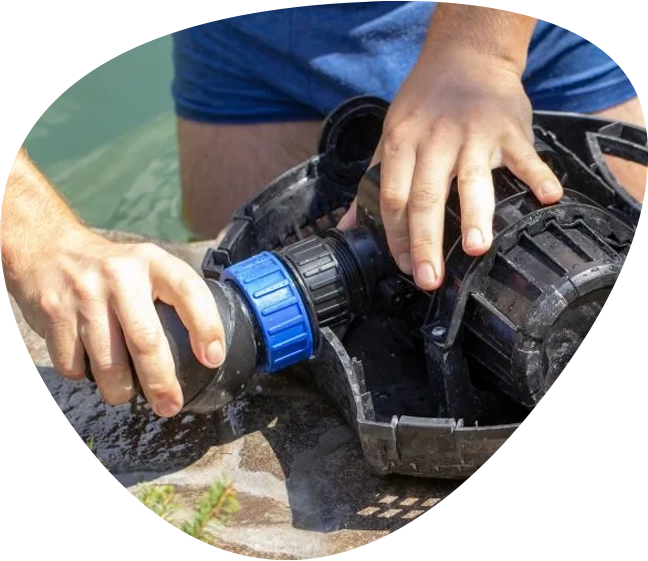
Pond Repair Services
Issues like a malfunctioning pump, clogged filter, or damaged liner can disrupt the balance and beauty of your pond.
We effectively carry out pond repairs to prolong the life of our pond systems and enhance the enjoyment and health of our aquatic life.





We are a Froglife Corporate Sponsor!
Our support will help Froglife protect frogs, toads, newts, snakes, and lizards and make a real difference in the lives of thousands of people who participate in Froglife projects every year.
Froglife is a national wildlife charity committed to the conservation of amphibians and reptiles – frogs, toads, newts, snakes and lizards – and saving the habitats they depend on.

Our Latest Posts
Pond Cleaning

Local Pond Cleaning Services for Effective Maintenance and Water Quality
Keeping a pond in good shape isn’t always easy....
Pond Maintenance

Pond Cleaning: Essential Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Water Garden
Keeping a pond clean matters for healthy water ...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Watford – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Watford, keeping it clean...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Experts Watford – Professional Solutions for Healthy, Beautiful Ponds
If you’ve got a pond in Watford—or you’re think...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Hemel Hempstead – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Hemel Hempstead, keeping ...
Koi Ponds

Most Expensive Koi Fish in the World: Record-Breaking Sales and Fascinating Facts
Koi fish hold a special place for collectors an...
Pond Cleaning
Pond Filtration
Pond Maintenance

Pond Maintenance, Pond Cleaning, Pond Repair, Pond Weed, Pond Problems: Essential Solutions for a Healthy Garden Pond
Pond maintenance and cleaning matter if we want...
Koi Ponds

Treat and prevent from gill flukes in the pond: Effective Strategies for Healthy Aquatic Life
Keeping pond fish healthy means staying aware o...
Pond Repair
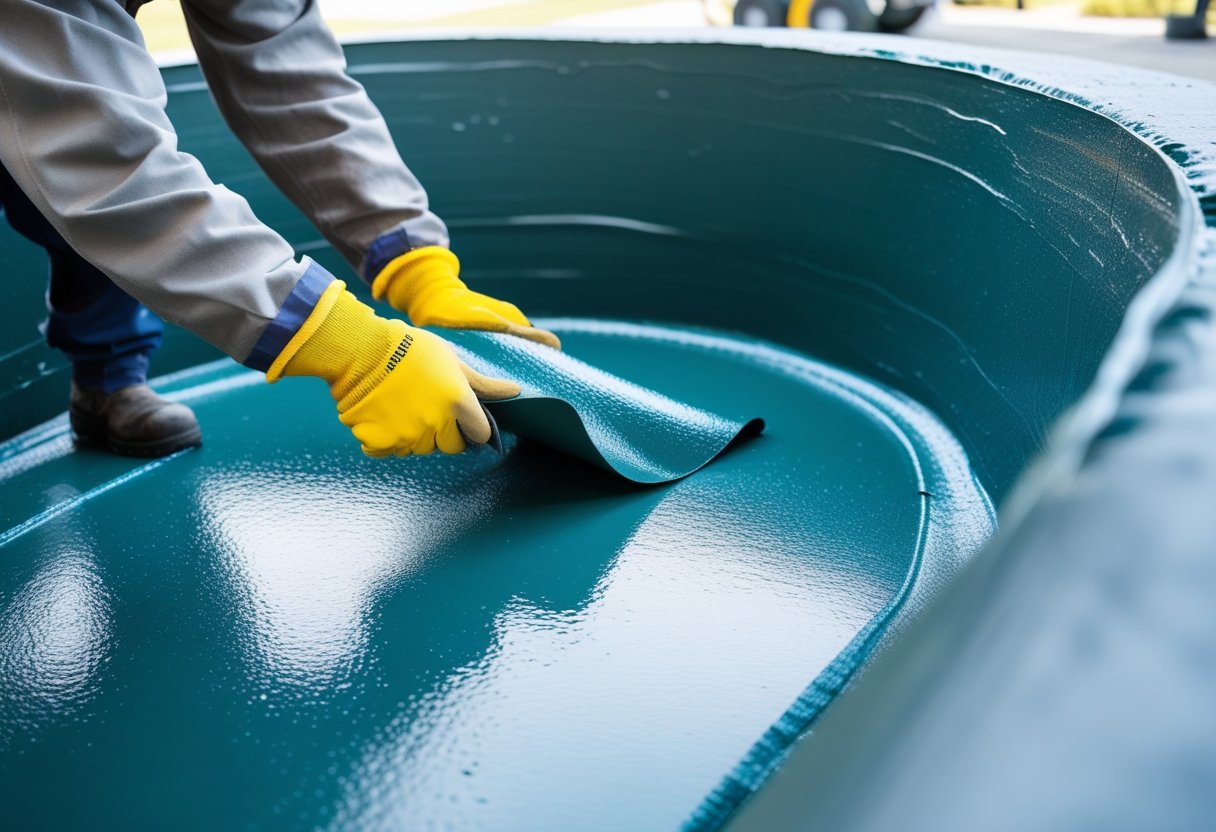

We Pond Fibreglassing Specialists in professional GRP fibreglass lining services for diverse client needs
If you want to keep your pond in great shape, ...
Pond Blog

Pond Cleaning Service: Essential Pond Maintenance and Filtration Systems for Monthly Care
How to Clean a Fish Pond Without Harming Your F...
Pond Blog

Fish Care Basics: Essential Tips for Keeping Your Pond Fish Happy and Healthy
Dealing With Sludge: How to Remove Muck from th...
Pond Blog

Pond Filter Guide: Choose the Right One to Keep Your Water Clean
Keeping a pond clean matters for water health a...
Pond Blog

Fall Pond Shutdown: Prepare Your Pond for Winter's Freeze
A stagnant pond quickly becomes an eyesore and ...
Pond Blog

DIY Pond Projects: Create Stunning Waterfalls and Efficient Bog Filters
We all want stunning, crystal clear water in ou...
Pond Blog

Pond Snails: Friend or Foe? Understanding Their Ecological Role
Maintaining a pond is not just about keeping it...
Pond Blog

Why You’ll Love The Aquascape Ion-Gen System For Your Pond: An Effective Solution for Water Quality Management
To keep our pond fish happy and healthy, we nee...
Pond Blog

Pond Aeration: The Crucial Role of Oxygen for a Thriving Ecosystem
Choosing the right pond filter is essential for...
Pond Blog

Pond Liner Repair: Fix Leaks Fast and Save Money with These Effective Solutions
Choosing the right pond cleaning company really...
Pond Blog

Dealing With Pond Predators: Effective Strategies to Safeguard Your Fish
As the leaves begin to fall and temperatures dr...
Pond Blog

Cost of Pond Ownership: Budget Planning to Avoid Unforeseen Expenses
What Is The Average Koi Pond Size? Understandin...
Pond Cleaning

Local Pond Cleaning Services for Effective Maintenance and Water Quality
Keeping a pond in good shape isn’t always easy....
Pond Maintenance

Pond Cleaning: Essential Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Water Garden
Keeping a pond clean matters for healthy water ...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Watford – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Watford, keeping it clean...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Experts Watford – Professional Solutions for Healthy, Beautiful Ponds
If you’ve got a pond in Watford—or you’re think...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Hemel Hempstead – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Hemel Hempstead, keeping ...
Koi Ponds

Most Expensive Koi Fish in the World: Record-Breaking Sales and Fascinating Facts
Koi fish hold a special place for collectors an...
Pond Cleaning
Pond Filtration
Pond Maintenance

Pond Maintenance, Pond Cleaning, Pond Repair, Pond Weed, Pond Problems: Essential Solutions for a Healthy Garden Pond
Pond maintenance and cleaning matter if we want...
Koi Ponds

Treat and prevent from gill flukes in the pond: Effective Strategies for Healthy Aquatic Life
Keeping pond fish healthy means staying aware o...
Pond Repair

We Pond Fibreglassing Specialists in professional GRP fibreglass lining services for diverse client needs
If you want to keep your pond in great shape, ...
Pond Blog

Pond Cleaning Service: Essential Pond Maintenance and Filtration Systems for Monthly Care
How to Clean a Fish Pond Without Harming Your F...
Pond Blog

Fish Care Basics: Essential Tips for Keeping Your Pond Fish Happy and Healthy
Dealing With Sludge: How to Remove Muck from th...
Pond Blog

Pond Filter Guide: Choose the Right One to Keep Your Water Clean
Keeping a pond clean matters for water health a...
Pond Blog

Fall Pond Shutdown: Prepare Your Pond for Winter's Freeze
A stagnant pond quickly becomes an eyesore and ...
Pond Blog

DIY Pond Projects: Create Stunning Waterfalls and Efficient Bog Filters
We all want stunning, crystal clear water in ou...
Pond Blog

Pond Snails: Friend or Foe? Understanding Their Ecological Role
Maintaining a pond is not just about keeping it...
Pond Blog

Why You’ll Love The Aquascape Ion-Gen System For Your Pond: An Effective Solution for Water Quality Management
To keep our pond fish happy and healthy, we nee...
Pond Blog

Pond Aeration: The Crucial Role of Oxygen for a Thriving Ecosystem
Choosing the right pond filter is essential for...
Pond Blog

Pond Liner Repair: Fix Leaks Fast and Save Money with These Effective Solutions
Choosing the right pond cleaning company really...
Pond Blog

Dealing With Pond Predators: Effective Strategies to Safeguard Your Fish
As the leaves begin to fall and temperatures dr...
Pond Blog

Cost of Pond Ownership: Budget Planning to Avoid Unforeseen Expenses
What Is The Average Koi Pond Size? Understandin...
Pond Cleaning

Local Pond Cleaning Services for Effective Maintenance and Water Quality
Keeping a pond in good shape isn’t always easy....
Pond Maintenance

Pond Cleaning: Essential Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Water Garden
Keeping a pond clean matters for healthy water ...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Watford – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Watford, keeping it clean...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Experts Watford – Professional Solutions for Healthy, Beautiful Ponds
If you’ve got a pond in Watford—or you’re think...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Hemel Hempstead – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Hemel Hempstead, keeping ...
Koi Ponds

Most Expensive Koi Fish in the World: Record-Breaking Sales and Fascinating Facts
Koi fish hold a special place for collectors an...
Pond Cleaning
Pond Filtration
Pond Maintenance

Pond Maintenance, Pond Cleaning, Pond Repair, Pond Weed, Pond Problems: Essential Solutions for a Healthy Garden Pond
Pond maintenance and cleaning matter if we want...
Koi Ponds

Treat and prevent from gill flukes in the pond: Effective Strategies for Healthy Aquatic Life
Keeping pond fish healthy means staying aware o...
Pond Repair

We Pond Fibreglassing Specialists in professional GRP fibreglass lining services for diverse client needs
If you want to keep your pond in great shape, ...
Pond Blog

Pond Cleaning Service: Essential Pond Maintenance and Filtration Systems for Monthly Care
How to Clean a Fish Pond Without Harming Your F...
Pond Blog

Fish Care Basics: Essential Tips for Keeping Your Pond Fish Happy and Healthy
Dealing With Sludge: How to Remove Muck from th...
Pond Blog

Pond Filter Guide: Choose the Right One to Keep Your Water Clean
Keeping a pond clean matters for water health a...
Pond Blog

Fall Pond Shutdown: Prepare Your Pond for Winter's Freeze
A stagnant pond quickly becomes an eyesore and ...
Pond Blog

DIY Pond Projects: Create Stunning Waterfalls and Efficient Bog Filters
We all want stunning, crystal clear water in ou...
Pond Blog

Pond Snails: Friend or Foe? Understanding Their Ecological Role
Maintaining a pond is not just about keeping it...
Pond Blog

Why You’ll Love The Aquascape Ion-Gen System For Your Pond: An Effective Solution for Water Quality Management
To keep our pond fish happy and healthy, we nee...
Pond Blog

Pond Aeration: The Crucial Role of Oxygen for a Thriving Ecosystem
Choosing the right pond filter is essential for...
Pond Blog

Pond Liner Repair: Fix Leaks Fast and Save Money with These Effective Solutions
Choosing the right pond cleaning company really...
Pond Blog

Dealing With Pond Predators: Effective Strategies to Safeguard Your Fish
As the leaves begin to fall and temperatures dr...
Pond Blog

Cost of Pond Ownership: Budget Planning to Avoid Unforeseen Expenses
What Is The Average Koi Pond Size? Understandin...
Pond Cleaning

Local Pond Cleaning Services for Effective Maintenance and Water Quality
Keeping a pond in good shape isn’t always easy....
Pond Maintenance

Pond Cleaning: Essential Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Water Garden
Keeping a pond clean matters for healthy water ...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Watford – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Watford, keeping it clean...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Experts Watford – Professional Solutions for Healthy, Beautiful Ponds
If you’ve got a pond in Watford—or you’re think...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Hemel Hempstead – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Hemel Hempstead, keeping ...
Koi Ponds

Most Expensive Koi Fish in the World: Record-Breaking Sales and Fascinating Facts
Koi fish hold a special place for collectors an...
Pond Cleaning
Pond Filtration
Pond Maintenance

Pond Maintenance, Pond Cleaning, Pond Repair, Pond Weed, Pond Problems: Essential Solutions for a Healthy Garden Pond
Pond maintenance and cleaning matter if we want...
Koi Ponds

Treat and prevent from gill flukes in the pond: Effective Strategies for Healthy Aquatic Life
Keeping pond fish healthy means staying aware o...
Pond Repair

We Pond Fibreglassing Specialists in professional GRP fibreglass lining services for diverse client needs
If you want to keep your pond in great shape, ...
Pond Blog

Pond Cleaning Service: Essential Pond Maintenance and Filtration Systems for Monthly Care
How to Clean a Fish Pond Without Harming Your F...
Pond Blog

Fish Care Basics: Essential Tips for Keeping Your Pond Fish Happy and Healthy
Dealing With Sludge: How to Remove Muck from th...
Pond Blog

Pond Filter Guide: Choose the Right One to Keep Your Water Clean
Keeping a pond clean matters for water health a...
Pond Blog

Fall Pond Shutdown: Prepare Your Pond for Winter's Freeze
A stagnant pond quickly becomes an eyesore and ...
Pond Blog

DIY Pond Projects: Create Stunning Waterfalls and Efficient Bog Filters
We all want stunning, crystal clear water in ou...
Pond Blog

Pond Snails: Friend or Foe? Understanding Their Ecological Role
Maintaining a pond is not just about keeping it...
Pond Blog

Why You’ll Love The Aquascape Ion-Gen System For Your Pond: An Effective Solution for Water Quality Management
To keep our pond fish happy and healthy, we nee...
Pond Blog

Pond Aeration: The Crucial Role of Oxygen for a Thriving Ecosystem
Choosing the right pond filter is essential for...
Pond Blog

Pond Liner Repair: Fix Leaks Fast and Save Money with These Effective Solutions
Choosing the right pond cleaning company really...
Pond Blog

Dealing With Pond Predators: Effective Strategies to Safeguard Your Fish
As the leaves begin to fall and temperatures dr...
Pond Blog

Cost of Pond Ownership: Budget Planning to Avoid Unforeseen Expenses
What Is The Average Koi Pond Size? Understandin...
Pond Cleaning

Local Pond Cleaning Services for Effective Maintenance and Water Quality
Keeping a pond in good shape isn’t always easy....
Pond Maintenance

Pond Cleaning: Essential Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Water Garden
Keeping a pond clean matters for healthy water ...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Watford – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Watford, keeping it clean...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Experts Watford – Professional Solutions for Healthy, Beautiful Ponds
If you’ve got a pond in Watford—or you’re think...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Hemel Hempstead – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Hemel Hempstead, keeping ...
Koi Ponds

Most Expensive Koi Fish in the World: Record-Breaking Sales and Fascinating Facts
Koi fish hold a special place for collectors an...
Pond Cleaning
Pond Filtration
Pond Maintenance

Pond Maintenance, Pond Cleaning, Pond Repair, Pond Weed, Pond Problems: Essential Solutions for a Healthy Garden Pond
Pond maintenance and cleaning matter if we want...
Koi Ponds

Treat and prevent from gill flukes in the pond: Effective Strategies for Healthy Aquatic Life
Keeping pond fish healthy means staying aware o...
Pond Repair

We Pond Fibreglassing Specialists in professional GRP fibreglass lining services for diverse client needs
If you want to keep your pond in great shape, ...
Pond Blog

Pond Cleaning Service: Essential Pond Maintenance and Filtration Systems for Monthly Care
How to Clean a Fish Pond Without Harming Your F...
Pond Blog

Fish Care Basics: Essential Tips for Keeping Your Pond Fish Happy and Healthy
Dealing With Sludge: How to Remove Muck from th...
Pond Blog

Pond Filter Guide: Choose the Right One to Keep Your Water Clean
Keeping a pond clean matters for water health a...
Pond Blog

Fall Pond Shutdown: Prepare Your Pond for Winter's Freeze
A stagnant pond quickly becomes an eyesore and ...
Pond Blog

DIY Pond Projects: Create Stunning Waterfalls and Efficient Bog Filters
We all want stunning, crystal clear water in ou...
Pond Blog

Pond Snails: Friend or Foe? Understanding Their Ecological Role
Maintaining a pond is not just about keeping it...
Pond Blog

Why You’ll Love The Aquascape Ion-Gen System For Your Pond: An Effective Solution for Water Quality Management
To keep our pond fish happy and healthy, we nee...
Pond Blog

Pond Aeration: The Crucial Role of Oxygen for a Thriving Ecosystem
Choosing the right pond filter is essential for...
Pond Blog

Pond Liner Repair: Fix Leaks Fast and Save Money with These Effective Solutions
Choosing the right pond cleaning company really...
Pond Blog

Dealing With Pond Predators: Effective Strategies to Safeguard Your Fish
As the leaves begin to fall and temperatures dr...
Pond Blog

Cost of Pond Ownership: Budget Planning to Avoid Unforeseen Expenses
What Is The Average Koi Pond Size? Understandin...
Pond Cleaning

Local Pond Cleaning Services for Effective Maintenance and Water Quality
Keeping a pond in good shape isn’t always easy....
Pond Maintenance

Pond Cleaning: Essential Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Water Garden
Keeping a pond clean matters for healthy water ...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Watford – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Watford, keeping it clean...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Experts Watford – Professional Solutions for Healthy, Beautiful Ponds
If you’ve got a pond in Watford—or you’re think...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Hemel Hempstead – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Hemel Hempstead, keeping ...
Koi Ponds

Most Expensive Koi Fish in the World: Record-Breaking Sales and Fascinating Facts
Koi fish hold a special place for collectors an...
Pond Cleaning
Pond Filtration
Pond Maintenance

Pond Maintenance, Pond Cleaning, Pond Repair, Pond Weed, Pond Problems: Essential Solutions for a Healthy Garden Pond
Pond maintenance and cleaning matter if we want...
Koi Ponds

Treat and prevent from gill flukes in the pond: Effective Strategies for Healthy Aquatic Life
Keeping pond fish healthy means staying aware o...
Pond Repair

We Pond Fibreglassing Specialists in professional GRP fibreglass lining services for diverse client needs
If you want to keep your pond in great shape, ...
Pond Blog

Pond Cleaning Service: Essential Pond Maintenance and Filtration Systems for Monthly Care
How to Clean a Fish Pond Without Harming Your F...
Pond Blog

Fish Care Basics: Essential Tips for Keeping Your Pond Fish Happy and Healthy
Dealing With Sludge: How to Remove Muck from th...
Pond Blog

Pond Filter Guide: Choose the Right One to Keep Your Water Clean
Keeping a pond clean matters for water health a...
Pond Blog

Fall Pond Shutdown: Prepare Your Pond for Winter's Freeze
A stagnant pond quickly becomes an eyesore and ...
Pond Blog

DIY Pond Projects: Create Stunning Waterfalls and Efficient Bog Filters
We all want stunning, crystal clear water in ou...
Pond Blog

Pond Snails: Friend or Foe? Understanding Their Ecological Role
Maintaining a pond is not just about keeping it...
Pond Blog

Why You’ll Love The Aquascape Ion-Gen System For Your Pond: An Effective Solution for Water Quality Management
To keep our pond fish happy and healthy, we nee...
Pond Blog

Pond Aeration: The Crucial Role of Oxygen for a Thriving Ecosystem
Choosing the right pond filter is essential for...
Pond Blog

Pond Liner Repair: Fix Leaks Fast and Save Money with These Effective Solutions
Choosing the right pond cleaning company really...
Pond Blog

Dealing With Pond Predators: Effective Strategies to Safeguard Your Fish
As the leaves begin to fall and temperatures dr...
Pond Blog

Cost of Pond Ownership: Budget Planning to Avoid Unforeseen Expenses
What Is The Average Koi Pond Size? Understandin...
Pond Cleaning

Local Pond Cleaning Services for Effective Maintenance and Water Quality
Keeping a pond in good shape isn’t always easy....
Pond Maintenance

Pond Cleaning: Essential Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Water Garden
Keeping a pond clean matters for healthy water ...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Watford – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Watford, keeping it clean...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Experts Watford – Professional Solutions for Healthy, Beautiful Ponds
If you’ve got a pond in Watford—or you’re think...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Hemel Hempstead – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Hemel Hempstead, keeping ...
Koi Ponds

Most Expensive Koi Fish in the World: Record-Breaking Sales and Fascinating Facts
Koi fish hold a special place for collectors an...
Pond Cleaning
Pond Filtration
Pond Maintenance

Pond Maintenance, Pond Cleaning, Pond Repair, Pond Weed, Pond Problems: Essential Solutions for a Healthy Garden Pond
Pond maintenance and cleaning matter if we want...
Koi Ponds

Treat and prevent from gill flukes in the pond: Effective Strategies for Healthy Aquatic Life
Keeping pond fish healthy means staying aware o...
Pond Repair

We Pond Fibreglassing Specialists in professional GRP fibreglass lining services for diverse client needs
If you want to keep your pond in great shape, ...
Pond Blog

Pond Cleaning Service: Essential Pond Maintenance and Filtration Systems for Monthly Care
How to Clean a Fish Pond Without Harming Your F...
Pond Blog

Fish Care Basics: Essential Tips for Keeping Your Pond Fish Happy and Healthy
Dealing With Sludge: How to Remove Muck from th...
Pond Blog

Pond Filter Guide: Choose the Right One to Keep Your Water Clean
Keeping a pond clean matters for water health a...
Pond Blog

Fall Pond Shutdown: Prepare Your Pond for Winter's Freeze
A stagnant pond quickly becomes an eyesore and ...
Pond Blog

DIY Pond Projects: Create Stunning Waterfalls and Efficient Bog Filters
We all want stunning, crystal clear water in ou...
Pond Blog

Pond Snails: Friend or Foe? Understanding Their Ecological Role
Maintaining a pond is not just about keeping it...
Pond Blog

Why You’ll Love The Aquascape Ion-Gen System For Your Pond: An Effective Solution for Water Quality Management
To keep our pond fish happy and healthy, we nee...
Pond Blog

Pond Aeration: The Crucial Role of Oxygen for a Thriving Ecosystem
Choosing the right pond filter is essential for...
Pond Blog

Pond Liner Repair: Fix Leaks Fast and Save Money with These Effective Solutions
Choosing the right pond cleaning company really...
Pond Blog

Dealing With Pond Predators: Effective Strategies to Safeguard Your Fish
As the leaves begin to fall and temperatures dr...
Pond Blog

Cost of Pond Ownership: Budget Planning to Avoid Unforeseen Expenses
What Is The Average Koi Pond Size? Understandin...
Pond Cleaning

Local Pond Cleaning Services for Effective Maintenance and Water Quality
Keeping a pond in good shape isn’t always easy....
Pond Maintenance

Pond Cleaning: Essential Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Water Garden
Keeping a pond clean matters for healthy water ...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Watford – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Watford, keeping it clean...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Experts Watford – Professional Solutions for Healthy, Beautiful Ponds
If you’ve got a pond in Watford—or you’re think...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Hemel Hempstead – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Hemel Hempstead, keeping ...
Koi Ponds

Most Expensive Koi Fish in the World: Record-Breaking Sales and Fascinating Facts
Koi fish hold a special place for collectors an...
Pond Cleaning
Pond Filtration
Pond Maintenance

Pond Maintenance, Pond Cleaning, Pond Repair, Pond Weed, Pond Problems: Essential Solutions for a Healthy Garden Pond
Pond maintenance and cleaning matter if we want...
Koi Ponds

Treat and prevent from gill flukes in the pond: Effective Strategies for Healthy Aquatic Life
Keeping pond fish healthy means staying aware o...
Pond Repair

We Pond Fibreglassing Specialists in professional GRP fibreglass lining services for diverse client needs
If you want to keep your pond in great shape, ...
Pond Blog

Pond Cleaning Service: Essential Pond Maintenance and Filtration Systems for Monthly Care
How to Clean a Fish Pond Without Harming Your F...
Pond Blog

Fish Care Basics: Essential Tips for Keeping Your Pond Fish Happy and Healthy
Dealing With Sludge: How to Remove Muck from th...
Pond Blog

Pond Filter Guide: Choose the Right One to Keep Your Water Clean
Keeping a pond clean matters for water health a...
Pond Blog

Fall Pond Shutdown: Prepare Your Pond for Winter's Freeze
A stagnant pond quickly becomes an eyesore and ...
Pond Blog

DIY Pond Projects: Create Stunning Waterfalls and Efficient Bog Filters
We all want stunning, crystal clear water in ou...
Pond Blog

Pond Snails: Friend or Foe? Understanding Their Ecological Role
Maintaining a pond is not just about keeping it...
Pond Blog

Why You’ll Love The Aquascape Ion-Gen System For Your Pond: An Effective Solution for Water Quality Management
To keep our pond fish happy and healthy, we nee...
Pond Blog

Pond Aeration: The Crucial Role of Oxygen for a Thriving Ecosystem
Choosing the right pond filter is essential for...
Pond Blog

Pond Liner Repair: Fix Leaks Fast and Save Money with These Effective Solutions
Choosing the right pond cleaning company really...
Pond Blog

Dealing With Pond Predators: Effective Strategies to Safeguard Your Fish
As the leaves begin to fall and temperatures dr...
Pond Blog

Cost of Pond Ownership: Budget Planning to Avoid Unforeseen Expenses
What Is The Average Koi Pond Size? Understandin...
Pond Cleaning

Local Pond Cleaning Services for Effective Maintenance and Water Quality
Keeping a pond in good shape isn’t always easy....
Pond Maintenance

Pond Cleaning: Essential Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Water Garden
Keeping a pond clean matters for healthy water ...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Watford – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Watford, keeping it clean...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Experts Watford – Professional Solutions for Healthy, Beautiful Ponds
If you’ve got a pond in Watford—or you’re think...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Hemel Hempstead – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Hemel Hempstead, keeping ...
Koi Ponds

Most Expensive Koi Fish in the World: Record-Breaking Sales and Fascinating Facts
Koi fish hold a special place for collectors an...
Pond Cleaning
Pond Filtration
Pond Maintenance

Pond Maintenance, Pond Cleaning, Pond Repair, Pond Weed, Pond Problems: Essential Solutions for a Healthy Garden Pond
Pond maintenance and cleaning matter if we want...
Koi Ponds

Treat and prevent from gill flukes in the pond: Effective Strategies for Healthy Aquatic Life
Keeping pond fish healthy means staying aware o...
Pond Repair

We Pond Fibreglassing Specialists in professional GRP fibreglass lining services for diverse client needs
If you want to keep your pond in great shape, ...
Pond Blog

Pond Cleaning Service: Essential Pond Maintenance and Filtration Systems for Monthly Care
How to Clean a Fish Pond Without Harming Your F...
Pond Blog

Fish Care Basics: Essential Tips for Keeping Your Pond Fish Happy and Healthy
Dealing With Sludge: How to Remove Muck from th...
Pond Blog

Pond Filter Guide: Choose the Right One to Keep Your Water Clean
Keeping a pond clean matters for water health a...
Pond Blog

Fall Pond Shutdown: Prepare Your Pond for Winter's Freeze
A stagnant pond quickly becomes an eyesore and ...
Pond Blog

DIY Pond Projects: Create Stunning Waterfalls and Efficient Bog Filters
We all want stunning, crystal clear water in ou...
Pond Blog

Pond Snails: Friend or Foe? Understanding Their Ecological Role
Maintaining a pond is not just about keeping it...
Pond Blog

Why You’ll Love The Aquascape Ion-Gen System For Your Pond: An Effective Solution for Water Quality Management
To keep our pond fish happy and healthy, we nee...
Pond Blog

Pond Aeration: The Crucial Role of Oxygen for a Thriving Ecosystem
Choosing the right pond filter is essential for...
Pond Blog

Pond Liner Repair: Fix Leaks Fast and Save Money with These Effective Solutions
Choosing the right pond cleaning company really...
Pond Blog

Dealing With Pond Predators: Effective Strategies to Safeguard Your Fish
As the leaves begin to fall and temperatures dr...
Pond Blog

Cost of Pond Ownership: Budget Planning to Avoid Unforeseen Expenses
What Is The Average Koi Pond Size? Understandin...
Pond Cleaning

Local Pond Cleaning Services for Effective Maintenance and Water Quality
Keeping a pond in good shape isn’t always easy....
Pond Maintenance

Pond Cleaning: Essential Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Water Garden
Keeping a pond clean matters for healthy water ...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Watford – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Watford, keeping it clean...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Experts Watford – Professional Solutions for Healthy, Beautiful Ponds
If you’ve got a pond in Watford—or you’re think...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Hemel Hempstead – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Hemel Hempstead, keeping ...
Koi Ponds

Most Expensive Koi Fish in the World: Record-Breaking Sales and Fascinating Facts
Koi fish hold a special place for collectors an...
Pond Cleaning
Pond Filtration
Pond Maintenance

Pond Maintenance, Pond Cleaning, Pond Repair, Pond Weed, Pond Problems: Essential Solutions for a Healthy Garden Pond
Pond maintenance and cleaning matter if we want...
Koi Ponds

Treat and prevent from gill flukes in the pond: Effective Strategies for Healthy Aquatic Life
Keeping pond fish healthy means staying aware o...
Pond Repair

We Pond Fibreglassing Specialists in professional GRP fibreglass lining services for diverse client needs
If you want to keep your pond in great shape, ...
Pond Blog

Pond Cleaning Service: Essential Pond Maintenance and Filtration Systems for Monthly Care
How to Clean a Fish Pond Without Harming Your F...
Pond Blog

Fish Care Basics: Essential Tips for Keeping Your Pond Fish Happy and Healthy
Dealing With Sludge: How to Remove Muck from th...
Pond Blog

Pond Filter Guide: Choose the Right One to Keep Your Water Clean
Keeping a pond clean matters for water health a...
Pond Blog

Fall Pond Shutdown: Prepare Your Pond for Winter's Freeze
A stagnant pond quickly becomes an eyesore and ...
Pond Blog

DIY Pond Projects: Create Stunning Waterfalls and Efficient Bog Filters
We all want stunning, crystal clear water in ou...
Pond Blog

Pond Snails: Friend or Foe? Understanding Their Ecological Role
Maintaining a pond is not just about keeping it...
Pond Blog

Why You’ll Love The Aquascape Ion-Gen System For Your Pond: An Effective Solution for Water Quality Management
To keep our pond fish happy and healthy, we nee...
Pond Blog

Pond Aeration: The Crucial Role of Oxygen for a Thriving Ecosystem
Choosing the right pond filter is essential for...
Pond Blog

Pond Liner Repair: Fix Leaks Fast and Save Money with These Effective Solutions
Choosing the right pond cleaning company really...
Pond Blog

Dealing With Pond Predators: Effective Strategies to Safeguard Your Fish
As the leaves begin to fall and temperatures dr...
Pond Blog

Cost of Pond Ownership: Budget Planning to Avoid Unforeseen Expenses
What Is The Average Koi Pond Size? Understandin...
Pond Cleaning

Local Pond Cleaning Services for Effective Maintenance and Water Quality
Keeping a pond in good shape isn’t always easy....
Pond Maintenance

Pond Cleaning: Essential Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Water Garden
Keeping a pond clean matters for healthy water ...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Watford – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Watford, keeping it clean...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Experts Watford – Professional Solutions for Healthy, Beautiful Ponds
If you’ve got a pond in Watford—or you’re think...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Hemel Hempstead – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Hemel Hempstead, keeping ...
Koi Ponds

Most Expensive Koi Fish in the World: Record-Breaking Sales and Fascinating Facts
Koi fish hold a special place for collectors an...
Pond Cleaning
Pond Filtration
Pond Maintenance

Pond Maintenance, Pond Cleaning, Pond Repair, Pond Weed, Pond Problems: Essential Solutions for a Healthy Garden Pond
Pond maintenance and cleaning matter if we want...
Koi Ponds

Treat and prevent from gill flukes in the pond: Effective Strategies for Healthy Aquatic Life
Keeping pond fish healthy means staying aware o...
Pond Repair

We Pond Fibreglassing Specialists in professional GRP fibreglass lining services for diverse client needs
If you want to keep your pond in great shape, ...
Pond Blog

Pond Cleaning Service: Essential Pond Maintenance and Filtration Systems for Monthly Care
How to Clean a Fish Pond Without Harming Your F...
Pond Blog

Fish Care Basics: Essential Tips for Keeping Your Pond Fish Happy and Healthy
Dealing With Sludge: How to Remove Muck from th...
Pond Blog

Pond Filter Guide: Choose the Right One to Keep Your Water Clean
Keeping a pond clean matters for water health a...
Pond Blog

Fall Pond Shutdown: Prepare Your Pond for Winter's Freeze
A stagnant pond quickly becomes an eyesore and ...
Pond Blog

DIY Pond Projects: Create Stunning Waterfalls and Efficient Bog Filters
We all want stunning, crystal clear water in ou...
Pond Blog

Pond Snails: Friend or Foe? Understanding Their Ecological Role
Maintaining a pond is not just about keeping it...
Pond Blog

Why You’ll Love The Aquascape Ion-Gen System For Your Pond: An Effective Solution for Water Quality Management
To keep our pond fish happy and healthy, we nee...
Pond Blog

Pond Aeration: The Crucial Role of Oxygen for a Thriving Ecosystem
Choosing the right pond filter is essential for...
Pond Blog

Pond Liner Repair: Fix Leaks Fast and Save Money with These Effective Solutions
Choosing the right pond cleaning company really...
Pond Blog

Dealing With Pond Predators: Effective Strategies to Safeguard Your Fish
As the leaves begin to fall and temperatures dr...
Pond Blog

Cost of Pond Ownership: Budget Planning to Avoid Unforeseen Expenses
What Is The Average Koi Pond Size? Understandin...
Pond Cleaning

Local Pond Cleaning Services for Effective Maintenance and Water Quality
Keeping a pond in good shape isn’t always easy....
Pond Maintenance

Pond Cleaning: Essential Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Water Garden
Keeping a pond clean matters for healthy water ...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Watford – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Watford, keeping it clean...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Experts Watford – Professional Solutions for Healthy, Beautiful Ponds
If you’ve got a pond in Watford—or you’re think...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Hemel Hempstead – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Hemel Hempstead, keeping ...
Koi Ponds

Most Expensive Koi Fish in the World: Record-Breaking Sales and Fascinating Facts
Koi fish hold a special place for collectors an...
Pond Cleaning
Pond Filtration
Pond Maintenance

Pond Maintenance, Pond Cleaning, Pond Repair, Pond Weed, Pond Problems: Essential Solutions for a Healthy Garden Pond
Pond maintenance and cleaning matter if we want...
Koi Ponds

Treat and prevent from gill flukes in the pond: Effective Strategies for Healthy Aquatic Life
Keeping pond fish healthy means staying aware o...
Pond Repair

We Pond Fibreglassing Specialists in professional GRP fibreglass lining services for diverse client needs
If you want to keep your pond in great shape, ...
Pond Blog

Pond Cleaning Service: Essential Pond Maintenance and Filtration Systems for Monthly Care
How to Clean a Fish Pond Without Harming Your F...
Pond Blog

Fish Care Basics: Essential Tips for Keeping Your Pond Fish Happy and Healthy
Dealing With Sludge: How to Remove Muck from th...
Pond Blog

Pond Filter Guide: Choose the Right One to Keep Your Water Clean
Keeping a pond clean matters for water health a...
Pond Blog

Fall Pond Shutdown: Prepare Your Pond for Winter's Freeze
A stagnant pond quickly becomes an eyesore and ...
Pond Blog

DIY Pond Projects: Create Stunning Waterfalls and Efficient Bog Filters
We all want stunning, crystal clear water in ou...
Pond Blog

Pond Snails: Friend or Foe? Understanding Their Ecological Role
Maintaining a pond is not just about keeping it...
Pond Blog

Why You’ll Love The Aquascape Ion-Gen System For Your Pond: An Effective Solution for Water Quality Management
To keep our pond fish happy and healthy, we nee...
Pond Blog

Pond Aeration: The Crucial Role of Oxygen for a Thriving Ecosystem
Choosing the right pond filter is essential for...
Pond Blog

Pond Liner Repair: Fix Leaks Fast and Save Money with These Effective Solutions
Choosing the right pond cleaning company really...
Pond Blog

Dealing With Pond Predators: Effective Strategies to Safeguard Your Fish
As the leaves begin to fall and temperatures dr...
Pond Blog

Cost of Pond Ownership: Budget Planning to Avoid Unforeseen Expenses
What Is The Average Koi Pond Size? Understandin...
Pond Cleaning

Local Pond Cleaning Services for Effective Maintenance and Water Quality
Keeping a pond in good shape isn’t always easy....
Pond Maintenance

Pond Cleaning: Essential Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Water Garden
Keeping a pond clean matters for healthy water ...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Watford – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Watford, keeping it clean...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Experts Watford – Professional Solutions for Healthy, Beautiful Ponds
If you’ve got a pond in Watford—or you’re think...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Hemel Hempstead – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Hemel Hempstead, keeping ...
Koi Ponds

Most Expensive Koi Fish in the World: Record-Breaking Sales and Fascinating Facts
Koi fish hold a special place for collectors an...
Pond Cleaning
Pond Filtration
Pond Maintenance

Pond Maintenance, Pond Cleaning, Pond Repair, Pond Weed, Pond Problems: Essential Solutions for a Healthy Garden Pond
Pond maintenance and cleaning matter if we want...
Koi Ponds

Treat and prevent from gill flukes in the pond: Effective Strategies for Healthy Aquatic Life
Keeping pond fish healthy means staying aware o...
Pond Repair

We Pond Fibreglassing Specialists in professional GRP fibreglass lining services for diverse client needs
If you want to keep your pond in great shape, ...
Pond Blog

Pond Cleaning Service: Essential Pond Maintenance and Filtration Systems for Monthly Care
How to Clean a Fish Pond Without Harming Your F...
Pond Blog

Fish Care Basics: Essential Tips for Keeping Your Pond Fish Happy and Healthy
Dealing With Sludge: How to Remove Muck from th...
Pond Blog

Pond Filter Guide: Choose the Right One to Keep Your Water Clean
Keeping a pond clean matters for water health a...
Pond Blog

Fall Pond Shutdown: Prepare Your Pond for Winter's Freeze
A stagnant pond quickly becomes an eyesore and ...
Pond Blog

DIY Pond Projects: Create Stunning Waterfalls and Efficient Bog Filters
We all want stunning, crystal clear water in ou...
Pond Blog

Pond Snails: Friend or Foe? Understanding Their Ecological Role
Maintaining a pond is not just about keeping it...
Pond Blog

Why You’ll Love The Aquascape Ion-Gen System For Your Pond: An Effective Solution for Water Quality Management
To keep our pond fish happy and healthy, we nee...
Pond Blog

Pond Aeration: The Crucial Role of Oxygen for a Thriving Ecosystem
Choosing the right pond filter is essential for...
Pond Blog

Pond Liner Repair: Fix Leaks Fast and Save Money with These Effective Solutions
Choosing the right pond cleaning company really...
Pond Blog

Dealing With Pond Predators: Effective Strategies to Safeguard Your Fish
As the leaves begin to fall and temperatures dr...
Pond Blog

Cost of Pond Ownership: Budget Planning to Avoid Unforeseen Expenses
What Is The Average Koi Pond Size? Understandin...
Pond Cleaning

Local Pond Cleaning Services for Effective Maintenance and Water Quality
Keeping a pond in good shape isn’t always easy....
Pond Maintenance

Pond Cleaning: Essential Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Water Garden
Keeping a pond clean matters for healthy water ...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Watford – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Watford, keeping it clean...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Experts Watford – Professional Solutions for Healthy, Beautiful Ponds
If you’ve got a pond in Watford—or you’re think...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Hemel Hempstead – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Hemel Hempstead, keeping ...
Koi Ponds

Most Expensive Koi Fish in the World: Record-Breaking Sales and Fascinating Facts
Koi fish hold a special place for collectors an...
Pond Cleaning
Pond Filtration
Pond Maintenance

Pond Maintenance, Pond Cleaning, Pond Repair, Pond Weed, Pond Problems: Essential Solutions for a Healthy Garden Pond
Pond maintenance and cleaning matter if we want...
Koi Ponds

Treat and prevent from gill flukes in the pond: Effective Strategies for Healthy Aquatic Life
Keeping pond fish healthy means staying aware o...
Pond Repair

We Pond Fibreglassing Specialists in professional GRP fibreglass lining services for diverse client needs
If you want to keep your pond in great shape, ...
Pond Blog

Pond Cleaning Service: Essential Pond Maintenance and Filtration Systems for Monthly Care
How to Clean a Fish Pond Without Harming Your F...
Pond Blog

Fish Care Basics: Essential Tips for Keeping Your Pond Fish Happy and Healthy
Dealing With Sludge: How to Remove Muck from th...
Pond Blog

Pond Filter Guide: Choose the Right One to Keep Your Water Clean
Keeping a pond clean matters for water health a...
Pond Blog

Fall Pond Shutdown: Prepare Your Pond for Winter's Freeze
A stagnant pond quickly becomes an eyesore and ...
Pond Blog

DIY Pond Projects: Create Stunning Waterfalls and Efficient Bog Filters
We all want stunning, crystal clear water in ou...
Pond Blog

Pond Snails: Friend or Foe? Understanding Their Ecological Role
Maintaining a pond is not just about keeping it...
Pond Blog

Why You’ll Love The Aquascape Ion-Gen System For Your Pond: An Effective Solution for Water Quality Management
To keep our pond fish happy and healthy, we nee...
Pond Blog

Pond Aeration: The Crucial Role of Oxygen for a Thriving Ecosystem
Choosing the right pond filter is essential for...
Pond Blog

Pond Liner Repair: Fix Leaks Fast and Save Money with These Effective Solutions
Choosing the right pond cleaning company really...
Pond Blog

Dealing With Pond Predators: Effective Strategies to Safeguard Your Fish
As the leaves begin to fall and temperatures dr...
Pond Blog

Cost of Pond Ownership: Budget Planning to Avoid Unforeseen Expenses
What Is The Average Koi Pond Size? Understandin...
Pond Cleaning

Local Pond Cleaning Services for Effective Maintenance and Water Quality
Keeping a pond in good shape isn’t always easy....
Pond Maintenance

Pond Cleaning: Essential Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Water Garden
Keeping a pond clean matters for healthy water ...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Watford – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Watford, keeping it clean...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Experts Watford – Professional Solutions for Healthy, Beautiful Ponds
If you’ve got a pond in Watford—or you’re think...
Pond Maintenance

Pond Services Hemel Hempstead – Expert Maintenance and Restoration Solutions
If you have a pond in Hemel Hempstead, keeping ...
Koi Ponds

Most Expensive Koi Fish in the World: Record-Breaking Sales and Fascinating Facts
Koi fish hold a special place for collectors an...
Pond Cleaning
Pond Filtration
Pond Maintenance

Pond Maintenance, Pond Cleaning, Pond Repair, Pond Weed, Pond Problems: Essential Solutions for a Healthy Garden Pond
Pond maintenance and cleaning matter if we want...
Koi Ponds

Treat and prevent from gill flukes in the pond: Effective Strategies for Healthy Aquatic Life
Keeping pond fish healthy means staying aware o...
Pond Repair

We Pond Fibreglassing Specialists in professional GRP fibreglass lining services for diverse client needs
If you want to keep your pond in great shape, ...
Pond Blog

Pond Cleaning Service: Essential Pond Maintenance and Filtration Systems for Monthly Care
How to Clean a Fish Pond Without Harming Your F...
Pond Blog

Fish Care Basics: Essential Tips for Keeping Your Pond Fish Happy and Healthy
Dealing With Sludge: How to Remove Muck from th...
Pond Blog

Pond Filter Guide: Choose the Right One to Keep Your Water Clean
Keeping a pond clean matters for water health a...
Pond Blog

Fall Pond Shutdown: Prepare Your Pond for Winter's Freeze
A stagnant pond quickly becomes an eyesore and ...
Pond Blog

DIY Pond Projects: Create Stunning Waterfalls and Efficient Bog Filters
We all want stunning, crystal clear water in ou...
Pond Blog

Pond Snails: Friend or Foe? Understanding Their Ecological Role
Maintaining a pond is not just about keeping it...
Pond Blog

Why You’ll Love The Aquascape Ion-Gen System For Your Pond: An Effective Solution for Water Quality Management
To keep our pond fish happy and healthy, we nee...
Pond Blog

Pond Aeration: The Crucial Role of Oxygen for a Thriving Ecosystem
Choosing the right pond filter is essential for...
Pond Blog

Pond Liner Repair: Fix Leaks Fast and Save Money with These Effective Solutions
Choosing the right pond cleaning company really...
Pond Blog

Dealing With Pond Predators: Effective Strategies to Safeguard Your Fish
As the leaves begin to fall and temperatures dr...
Pond Blog

Cost of Pond Ownership: Budget Planning to Avoid Unforeseen Expenses
What Is The Average Koi Pond Size? Understandin...

Why Choose Us
Experience With years of experience in pond maintenance and cleaning, our team has the expertise to handle ponds of all sizes and complexities. We are dedicated to delivering high-quality services tailored to meet the unique needs of each customer.
Professionalism Our team consists of trained professionals who are passionate about pond care. We take pride in our work and strive to exceed our customers’ expectations with every service we provide.
Customized Solutions We understand that every pond is different, and we tailor our services to suit the specific requirements of each customer. Whether you have a small backyard pond or a larger water feature, we have the knowledge and resources to keep it in pristine condition.
Environmentally Friendly Practices We are committed to using eco-friendly products and methods in our pond cleaning services. Our goal is to promote sustainability and preserve the natural balance of your pond ecosystem.
Customer Satisfaction Your satisfaction is our top priority. We work closely with our customers to ensure that their pond maintenance needs are met with professionalism and care. We take the time to listen to your concerns and provide personalized recommendations to help you achieve the pond of your dreams.
Ready to schedule a pond cleaning service with us?
Contact Aqua Pond today to learn more about our services and to book an appointment.
Let us help you create a clean, healthy, and vibrant pond that you can enjoy for years. Thank you for considering Aqua Pond for your pond maintenance needs.
What our Customers Say...
